5 Major 3D Printing Trends to Look for In 2023
The new year has begun, and it’s time to take a look at the 3D printing trends shaping the industry. Last year was again challenging, with ongoing supply chain disruptions, the war in Ukraine and the associated rise in energy and raw material prices. It had shown that the importance of reducing costs and increasing supply chain resilience remains high and that 3D printing can play a huge role in facing those challenges. Here are 5 trends we have identified that will have huge impact on the 3D printing industry this year and beyond.
Wider range of 3D printing use cases due to increasing technology maturity
As more innovative materials arise, the technology will become available for more applications in industries such as healthcare, manufacturing, agriculture, and transportation. Companies are increasingly shifting their additive manufacturing processes from prototyping to volume production. In doing so, companies use 3D printing as a replacement for traditional manufacturing or as so-called “bridge manufacturing” to bridge the gap between supply and demand. At times when supply chain disruptions are occurring and certain parts and raw materials have immense lead times, the technology is enabling the rapid availability of much-needed parts. Also for production ramp-up and spare parts for older products additive manufacturing is an optimal solution. Service bureaus or 3D printing platforms will play an important role in scaling the business and fulfilling all application needs in 2023. They enable the easy shift from one material and technology to another and decrease the risk and cost of implementing own infrastructure.

The rise of the digital supply chain
The increasing use of 3D printing is driving the need for streamlined processes for greater efficiency and cost reduction. In 2023, the trend goes towards more automated and integrated AM workflows. They combine production and supply chain and connect all 3D printing players on the market, such as software providers, print farms customers and post-processing and material specialists.
3D printing part identification software will become increasingly common to quickly evaluate the 3D printability out of a large list of parts. And digital warehousing platforms will enable companies to manage their parts more efficiently throughout their lifecycle. On one side companies can eliminate warehousing and start production on-demand. On the other side it enables them to directly order parts through an integrated or connected ordering system, and have them produced decentrally. All in all, a digital supply chain that uses additive manufacturing technologies will lead to much more transparency, sustainability, flexibility and efficiency.
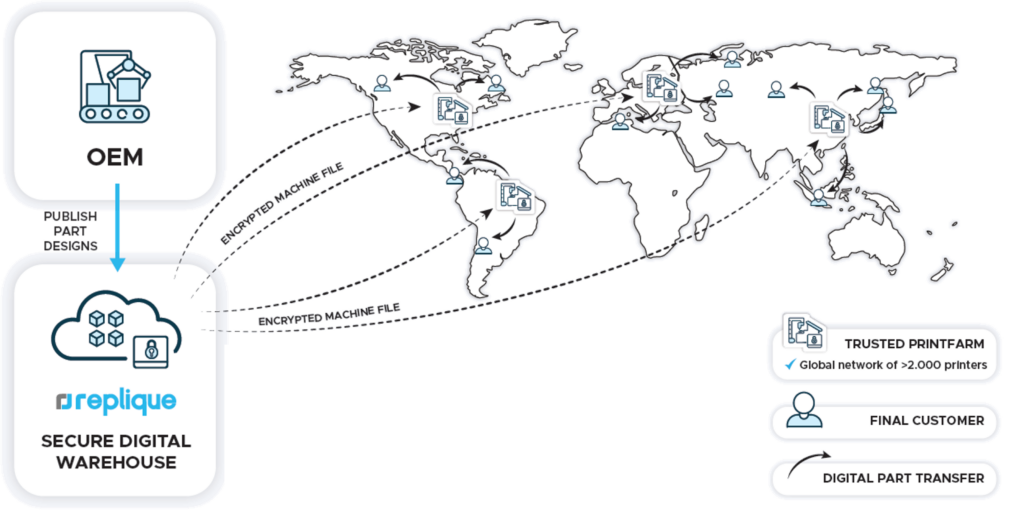
Quality assurance as the foundation of industrial 3D printing
Another emerging 3D printing trend that comes with the industrial use of additive manufacturing is the implementation of secure processes, certified materials and adequate technologies. 3D printing must ensure process repeatability and each part must meet the same quality requirements.
That’s why at Replique we introduced the quality assurance module RSure on our end-to-end 3D printing platform. The tool allows OEMs to digitally define quality requirements and an inspection process (e.g. dimensions, photo documentation, …) that 3D printing service providers must perform before shipping the part. The production information of each produced part is centrally stored on the platform as part of the “digital twin”. This enables seamless part documentation and the use of a decentralized 3D printing platform on an industrial scale.

To improve stability of AM processes, we further see an emerging trend to use AI to control digital manufacturing. AI will help monitor, collect, and analyze machine data in-situ to avoid and fix errors and enable reliability and repeatability of AM processes.
Sustainability in additive manufacturing
The trend towards greater sustainability will continue to shape 2023 and new arising innovations. AM will become a more dominant technology to achieve sustainability goals by reducing the CO2 footprint of parts significantly in various aspects:
- No overproduction (produce only the needed parts on-demand)
- No need to scrap products because of missing spares
- Reduced transportation efforts
The ability to redesign parts to be lighter and stronger will also have a positive impact on the sustainability of 3D printing as more use cases are developed specifically for 3D printing within the coming years. We also see a trend toward more sustainable materials, such as recyclable and bio derived materials. Service providers have to make these positive impacts more measurable through software in 2023.
All in all, the sustainability benefits will also meet end customer requirements who are beginning to demand product sustainability, as evidenced e.g. by the current “Right to Repair” movement, which calls for repairable products and spare parts for the entire life of products.

Metal 3D printing as a rising trend
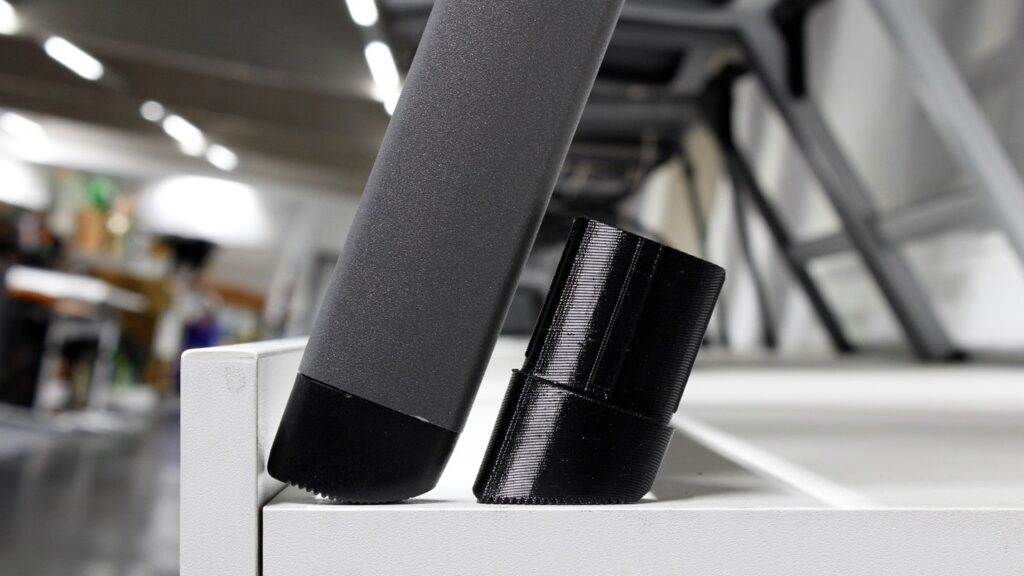
Looking at material and technology trends in 2023, we see above all an increasing use of metal 3D printing. This enables the production of complex metal parts with greatly reduced waste and lower costs compared to traditional manufacturing. Metal polymers in particular have made their way into the market and will continue to grow in 2023. This offers the opportunity to manufacture metal parts with filaments. The filaments contain metal and polymer particles, but the polymer particles are removed in the debinding and sintering process after the printing by heating the part. The ability to print parts with metal filaments currently has design limitations and is only suitable for smaller parts with designs that are not very complex. However, for suitable parts, metal filaments are a very good alternative to traditional metal AM technologies such as SLM, especially for financial reasons.
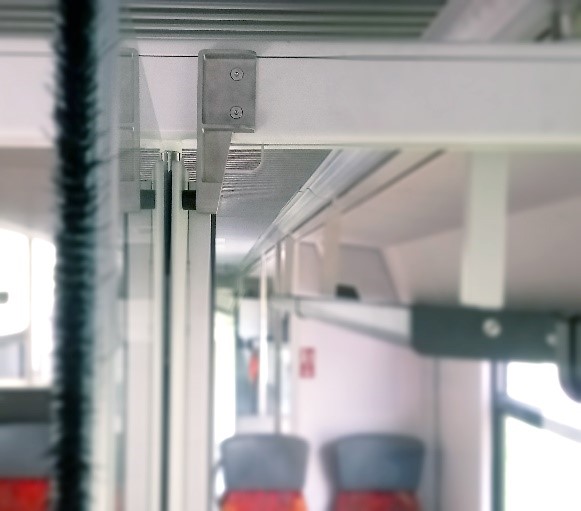
At Replique, we have already made use of the technology, including a collaboration with Alstom, a global leader in green and smart mobility. Here, for the first time, we have qualified and produced a visible metal part for additive series manufacturing. The parts are made of Ultrafuse 316L stainless steel using metal FDM technology as a cost-effective and fast solution.

Conclusion: A glance at the future of 3D printing
Although times keep uncertain in 2023, we are sure that 3D printing will influence global production market in a positive way, with increased sustainability, resilience, and reduced costs. However, to really reach industrial status, standardized processes and assured quality are needed, including ways to track and control print quality. We see a strong trend towards digital processes that connect and streamline all processes from selecting, storing, ordering and tracking parts via 3D printing to fulfill this goal.
Want to jump on the trends and make use of 3D printing in the easiest and most cost-efficient way?
Then contact us to discuss your possibilities with an end-to-end digital inventory platform!
Categories
- 3D printing industries (6)
- 3D Printing Materials (1)
- Basics (3)
- News (1)
- Point of View (10)
- Press (20)
- Press (20)
- Sustainability (3)
- Technology (6)
- Uncategorized (1)
- White Paper (1)



