How to Leverage 3D Printing in Robotics and Automation
In the ever-evolving landscape of production and logistics, robotics & automation play an increasingly vital role, driven by the wave of digitization. However, as with any technology, there are also hurdles which have to be overcome, especially when it comes to the production of customized and lightweight parts in a cost-efficient manner. This is where 3D printing steps in. Join us in this blog article as we explore the benefits and diverse applications of 3D printing for robotic parts and learn about the connection of those two technologies.
Understanding 3D Printing
Before exploring their interconnection, let’s understand 3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing. Additive manufacturing enables the conversion of digital designs into tangible objects by building up layers of material. You just need the right design and production can start without any huge production ramp-up. This freedom enables intricate designs, rapid prototyping, and on-demand production of customized parts, offering a level of flexibility and innovation that has redefined the manufacturing landscape.

Custom Parts with 3D Printing
Robotics is one of the industries, where these benefits of 3D printing can play a crucial role. And there are many reasons for it. One is the possibility to create custom parts of robotics and automation machinery using 3D printing. Traditional manufacturing methods often fall short when it comes to creating parts, such as grippers, tailored to specific tasks without incurring exorbitant costs due to the creation of specialized tools and molds. Thanks to 3D printing, even small players (SMEs), can use 3D printing to create budget-friendly robot parts, as there are no minimum order quantity, meaning they can produce parts starting from lot-size one.

Lightweight Parts Thanks to Intricate Designs
Weight is a critical factor in optimizing robotic performance. Traditional manufacturing often results in excess weight due to subtractive processes. 3D printing revolutionizes this by allowing engineers to design intricate, hollow structures, optimizing weight without compromising strength. This newfound agility finds applications in drones, exoskeletons, and various robotic systems.
Part Consolidation and Modulation
3D printing’s technical benefit extends to the consolidation of multiple parts into a single, complex structure. This not only reduces overall weight but also minimizes assembly challenges and inventory complexity. On the other side, 3D printing allows the separation of a single part into distinct components, simplifying modifications if needed.
Quick Prototyping and Design Changes
Compared to traditional methods, 3D printing offers unparalleled agility in prototyping and design alterations. Engineers and designers can swiftly translate conceptual ideas into tangible prototypes. This means they can test a prototype out almost immediately to see if it’s a good fit. And if they want to tweak or change the design, they can easily do that thanks to the flexibility of 3D printing, empowering innovators to adapt and optimize robotic components with unprecedented speed. This not only accelerates the product development cycle and reduces time-to-market considerably, but also fosters a culture of continuous improvement in the ever-evolving field of robotics.
Spare Parts On-Demand
The wear and tear faced by robotics and automation machinery can lead to costly downtime. Traditional methods of obtaining spare parts involve a time-consuming process of ordering, shipping, and, in some cases, custom manufacturing.
3D printing provides a rapid and cost-effective solution for local or even on-site production of spare parts, just on-demand. Instead of waiting for shipments or relying on extensive inventories, robots can be quickly restored to operational status with 3D printed replacements. This capability significantly minimizes downtime, ensuring continuous robot functionality.

Learn more about the benefits of 3D printing for the production of spare parts.
Application examples
Grippers
Especially, grippers, are undergoing a revolution thanks to additive manufacturing. It enables the creation of grippers in small volumes that are not only cost-efficient but also remarkably lightweight and optimized. When the need arises to change grippers, 3D printing facilitates a swift process with short development and production times. This capability translates into faster movements, reduced cycle times, and an overall more agile manufacturing process.
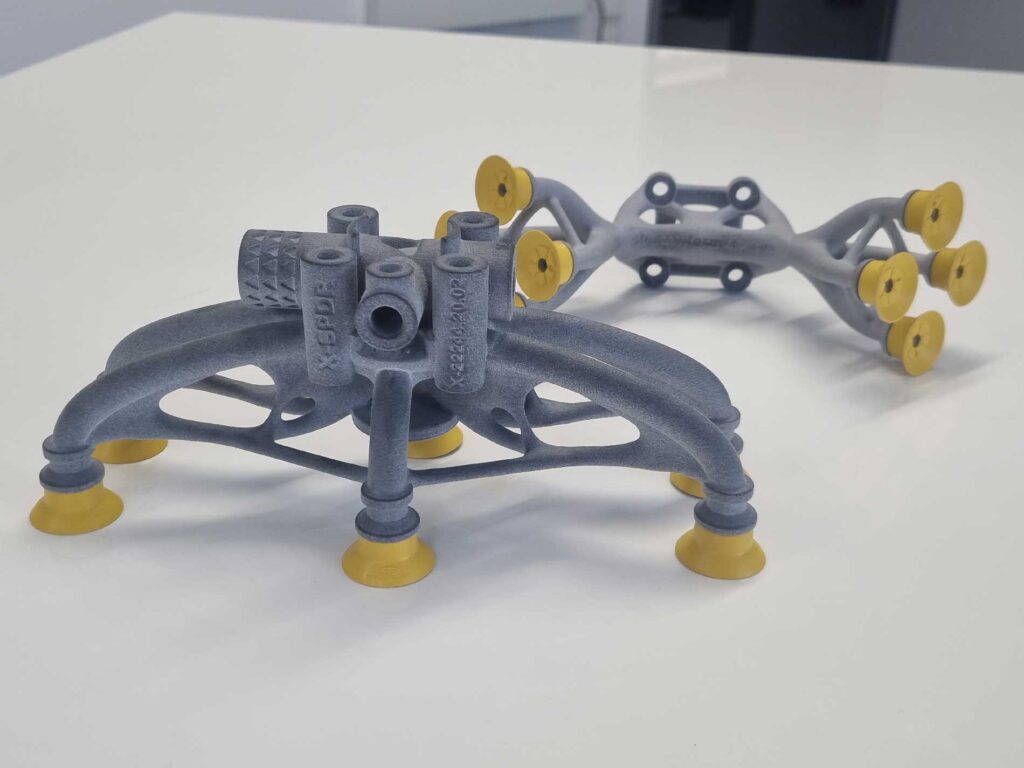

In a recent cooperation with struktur.form.design Engineering GmbH for example, we were able to reduce weight of a cobot gripper by 78%, part count by 84% and overall production cost savings by 30%, just via redesigning and producing via additive manufacturing.
And the benefits extend beyond industrial automation, making a significant impact on healthcare robotics as well. In surgical robots, for instance, 3D printed grippers can handle specialized instruments and execute delicate tasks.
Embedded sensors and electronic components
Beyond these core connections, the collaboration between 3D printing and robotics unfolds into an expansive canvas of possibilities. For example, embedding sensors and electronic components directly into robotic structures using 3D printing enhances their functionality and streamlines assembly processes.
Soft robotics
For soft robotics – those dealing with flexible and deformable structures – 3D printing opens avenues for the creation of parts that move and adapt like real muscles. Researchers from the Delft University of Technology, for instance, have pioneered the use of 3D printing in manufacturing soft robots with intricate viscoelastic hydrogels. These materials withstand high pressures and open new possibilities in fields like medical prosthetics.
Innovation and Education
Moreover, 3D printing serves as a catalyst for innovation and education in robotics. It fosters creativity among students and researchers, accelerating the learning curve and driving advancements in the development of robotic systems.
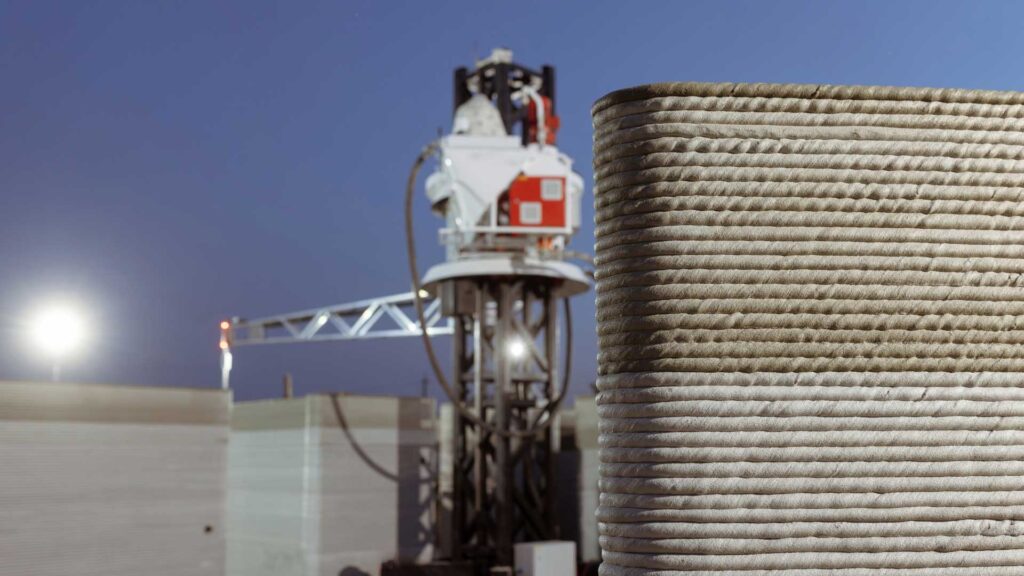
Robots as 3D Printers
The marriage of robotics and 3D printing can even extend beyond conventional roles. Here, robots themselves become integral 3D printers, amplifying the scope and scale of additive manufacturing. Especially noteworthy in large-scale 3D printing, robotic arms deposit materials layer by layer to create objects. This facilitates the creation of parts on a scale previously unattainable in 3D printing.

Conclusion
The intersection of 3D printing and robotics reshapes how we conceive, design, and build robotic systems. From lightweight components to customized grippers and on-demand spare parts, this collaboration represents a paradigm shift, offering tailored solutions that enhance the efficiency and adaptability of robotic systems.
Categories
- 3D printing industries (6)
- 3D Printing Materials (1)
- Basics (3)
- News (1)
- Point of View (10)
- Press (20)
- Press (20)
- Sustainability (3)
- Technology (6)
- Uncategorized (1)
- White Paper (1)


