7 Trends Shaping the 3D Printing Landscape in 2024 and Beyond
As the manufacturing landscape continues to evolve, 3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing (AM), stands out as a transformative force driving innovation across industries. The year 2023 marked significant advancements in 3D printing technology, with notable progress in printing speed, precision, and the development of specialized materials. From aerospace to healthcare, 3D printing is revolutionizing manufacturing processes, offering unparalleled flexibility and efficiency. As we anticipate the future of this technology, let’s dive into the key trends in 2024 and beyond.
1. Shift Towards Serial Production
While 3D printing was initially utilized for rapid prototyping and low-volume manufacturing, advancements in printing speed, precision, and material properties have made it viable for large-scale production, and the technology is increasingly used for serial production. Companies across industries are leveraging 3D printing to streamline production processes, reduce costs, and accelerate time-to-market. From automotive manufacturers producing custom car parts to automation companies manufacturing complex components, serial production with 3D printing offers unparalleled flexibility and efficiency. The shift towards serial production emphasizes that qualified production processes and materials will play an important role in meeting stringent industry standards and ensuring the reliable performance of end-use parts across a range of industries.
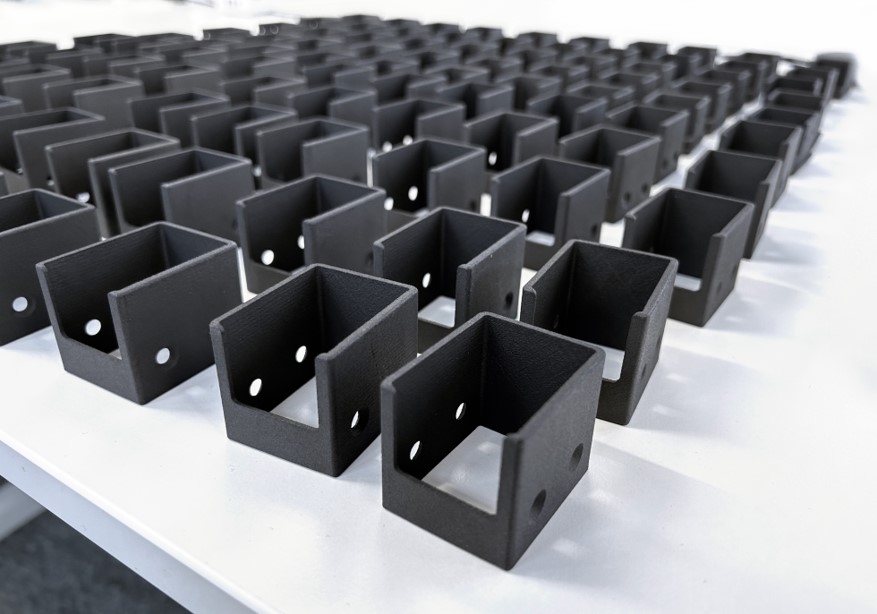
2. Rise of Specialized 3D Printing Materials

As industries are increasingly recognizing additive manufacturing as a serious production technology for end-use parts, they require materials tailored and certified for specific applications. These specialized materials offer unique properties such as enhanced strength, flexibility, conductivity, or biocompatibility, unlocking new possibilities for applications across industries. For example, in the aerospace sector, the development of lightweight yet durable materials has revolutionized the production of aircraft components, leading to increased fuel efficiency and reduced emissions. Further evidence for this trend can be seen in the growing popularity of flame-retardant, food-grade, and sustainable materials. There is an increasing focus on providing not only diverse material options but also ensuring that these materials meet advanced performance criteria across a range of industries.
3. The Need for Standardized Processes
Despite progress, challenges persist in scaling up 3D printing for mass production. Standardizing processes and achieving greater uniformity in materials and machines remain key priorities for the industry. Manufacturers face hurdles in identifying and qualifying parts for 3D printing, highlighting the need for informed selection processes and platforms facilitating material qualification. However, collaborative efforts and innovative solutions are paving the way for overcoming these challenges, unlocking new opportunities for manufacturers to enhance competitiveness and efficiency.

4. Market Consolidation and Industry Collaboration
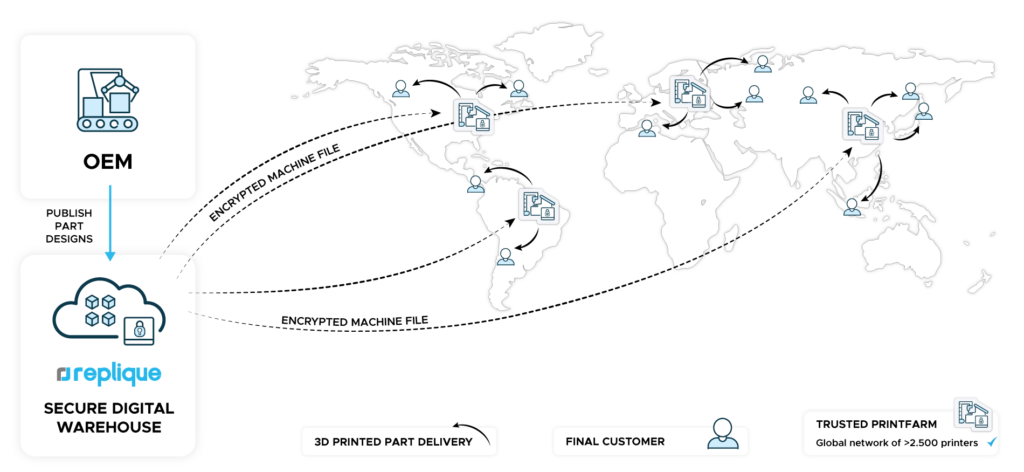
As the 3D printing industry continues to mature, we are witnessing a trend towards market consolidation and industry collaboration, where key players merge or acquire other market participants. In recent years, centralized platforms and end-to-end solutions have emerged, connecting all stakeholders in the manufacturing ecosystem, from material suppliers to 3D printing service providers. This consolidation not only addresses the challenge of fragmentation but also fosters collaboration, transparency, and efficiency. By standardizing processes, sharing best practices, and pooling resources, companies can unlock new opportunities for innovation and growth in the 3D printing market.

5. Integration of Artificial Intelligence and Automation
The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and automation technologies is set to revolutionize the 3D printing process, optimizing efficiency and precision. AI algorithms will play a greater role in optimizing the entire 3D printing process, from part selection to design conceptualization, production, and post-processing. This advancement ensures greater precision and efficiency as machines learn and adapt to evolving requirements.
Furthermore, the implementation of predictive maintenance strategies combined with on-demand 3D printing will minimize downtime and enhance manufacturing responsiveness. Connected 3D printers will be able to proactively produce spare parts as needed, contributing to a more streamlined and responsive manufacturing ecosystem.
6. Increasing Sustainability Concerns

In an era marked by growing environmental concerns, sustainability has become a top priority for businesses worldwide. 3D printing offers a sustainable alternative to traditional manufacturing methods. With the ability to produce parts on-demand and localize manufacturing, 3D printing reduces the need for mass production, warehousing, and long-distance shipping, resulting in significant reductions in energy consumption and environmental impact. Furthermore, this emphasis on sustainability aligns with the evolving customer demand on the Right to Repair, supported by EU‘s Right to Repair regulations. By providing the capability to produce replacement parts on-demand, 3D printing facilitates the repair and extension of the lifespan of products, contributing to a more sustainable and circular economy. Additionally, the use of biodegradable and recycled materials further enhances the sustainability of 3D printing, driving a shift towards more eco-friendly manufacturing practices.
7. Reduction of Supply Chain Disruptions and Associated Risks
Another notable trend for 2024 is the strategic use of 3D printing to mitigate supply chain and financial risks in manufacturing. Industries of all kinds are facing supply chain disruptions (e.g. Huthi and Panama Canal), imposing severe risks even to established players such as Ikea and Tesla. The ability to produce on-demand and decentrally allows for more agile and responsive supply chains, reducing the need for large inventories and associated capital expenditures. Companies embracing 3D printing can potentially decrease the financial risk associated with overstocked inventories, aligning their production more closely with actual demand. This flexibility contributes to a more adaptive and cost-effective approach, especially in uncertain economic environments.
Conclusion: Embracing the Future of Manufacturing
As we look ahead to 2024 and beyond, the future of additive manufacturing is not only fueled by growth, but also maturation. From breakthroughs in materials science to advancements in sustainability and supply chain resilience, 3D printing is reshaping the way we design, produce, and distribute goods. By embracing these trends and leveraging the capabilities of 3D printing, manufacturers can unlock new opportunities for innovation, efficiency, and sustainability in the dynamic landscape of manufacturing.
Categories
- 3D printing industries (6) 6
- 3D Printing Materials (1) 1
- Basics (3) 3
- News (1) 1
- Point of View (10) 10
- Press (20) 20
- Press (20) 20
- Sustainability (3) 3
- Technology (6) 6
- Uncategorized (1) 1
- White Paper (1) 1



